Brain Surgery
Carewell Neuro Spine Center offers comprehensive evaluation, diagnosis, and surgical treatment of diseases of the brain.
Brain tumor surgeon in Aurangabad
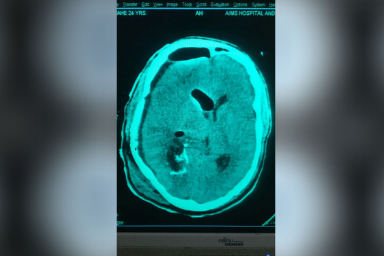
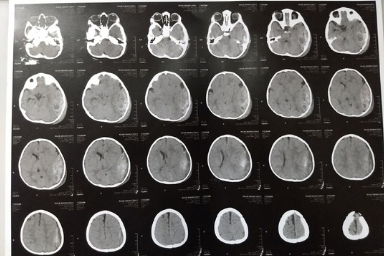
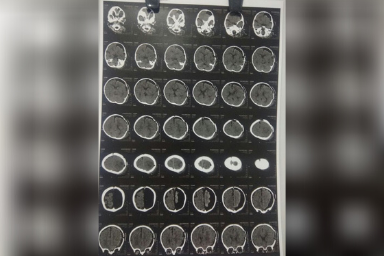
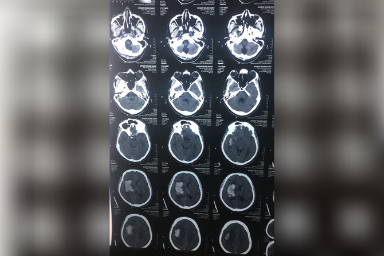
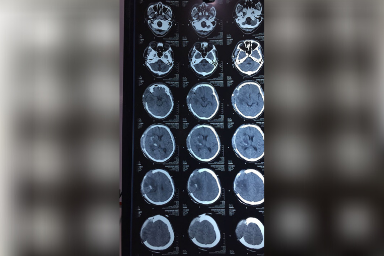
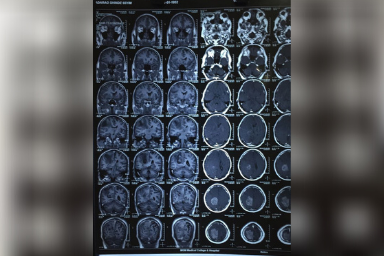
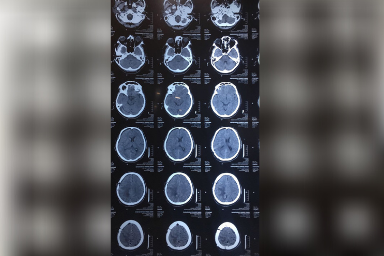
Carewell Neuro Spine Center provides extensive brain disease evaluation, diagnosis, and surgical treatment. These involve hydrocephalus, vascular disease, stroke, pituitary tumors, and brain tumors, as well as bleeding in or around the brain (intracerebral hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, and epidural hemorrhage). We have success in both non-surgical and surgical treatments. We use the most up-to-date testing techniques to quickly assess a patient’s correct diagnosis. If surgery is necessary, Dr. Sushil Shinde employs state-of-the-art technology in the operating room to ensure a good outcome. Dr. Sushil Shinde is One of the Best Brain tumor Surgeon in Aurangabad and He is the Consultant Neurosurgeon in Aurangabad at Carewell Superspeciality Hospital. He uses minimally invasive brain surgery to achieve the least brain disturbance, pain, and scarring and to facilitate the quickest recovery possible. We measure our success by our ability to treat the disease successfully and help our patients return quickly to normal life.
Dr. Sushil Shinde of Carewell Hospital offers world-class tertiary treatment for all types of neurological problems, illnesses, and diseases, including brain tumors. He is one of the leading Brain tumor surgeon in Aurangabad. Their fast, accurate brain tumor diagnosis and treatment have resulted in high success rates and saved the lives of countless individuals.
Particular brain conditions we treat and procedures we perform include:
• Subdural hematoma
• Epidural hematoma
• Intracerebral bleeding
• Hydrocephalus
• Stroke
• Vascular disease
• Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
• Chiari Malformation
• Trigeminal Neuralgia
• Head trauma
• Concussion
• Craniotomy
• Cranioplasty
• Ventriculostomy
• Burr holes
• Ventricular Peritoneal Shunt
• Microvascular Decompression
• Transphenoidal Surgery
FAQ's
A brain tumor is a development of cells or tissue in the brain or the skull vault that is abnormal. It is caused by an abnormal and unregulated cell division, which occurs most commonly in the brain, but can also occur in lymphatic tissue, blood vessels, cranial nerves, brain meninges (a thin layer of tissue that covers the spinal cord and brain), the skull, pituitary gland, or pineal gland, as well as from congenital vest cells.
There are many different types of brain tumors, and they all fall into one of the following groups:
Benign Tumor: It’s a benign tumor, which means it’s not cancerous. A benign tumor must be carefully examined to see if it is near critical structures like blood arteries, nerves, or the brain stem.
Malignant Tumor: The term “malignant tumor” refers to a tumor that is cancerous in nature. It is critical to evaluate if a malignant tumor is primary or metastatic. The size, nature, and location of the tumor all play a role in determining the best treatment option.
Metastatic Tumor: A malignant brain tumor produced by the spread of cancer cells from another part of the body is referred to as a metastatic tumor. The lung, breast, kidney, colon, or metastatic melanoma are frequently the initial cause (primary location) of metastatic brain tumors. Some people may experience symptoms from metastatic brain tumors before the source site is identified. In around 90% of patients, the primary source of the metastatic tumor may be identified.
While doctors have yet to discover the etiology of primary brain tumors, they have discovered a number of risk factors that make you susceptible to brain tumors.
Radiation: Radiation is one of the most well-known hazards associated with a brain tumor. People with a history of cancer who have received radiation repeated computerized tomography (CT scans), or X-rays to the head are at a higher risk of developing brain tumors.
Genetic Diseases: Certain genetic diseases can increase your risk of developing a brain tumor. Neurofibromatosis is a tumor-causing genetic disorder, Turcot syndrome is characterized by aberrant cells, Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome is characterized by abnormal cells, and Li-Fraumeni syndrome is characterized by aberrant cells.
HIV or AIDS: People with HIV or AIDS are more susceptible to brain tumors than others because their immune systems are compromised.
The type and intensity of symptoms are determined by the brain tumor’s size, nature, and location. The following are some of the most common signs and symptoms:
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty in writing or reading
- Weakness
- Lack of bladder/bowel control
- Vision problems
- Seizures (especially in older adults)
- Change in personality, mood, behaviour or emotional changes
- Confusion Difficulty with memory or the ability to understand
- Decreased level of consciousness
- Hearing loss with or without recurrent giddiness